Understanding the Magnificent Of Uranium On The Earth

Uranium is a chemical element in the periodic table with the symbol U and atomic number 92. The substance is characterized by its weight, silvery-white color, toxic properties, metallic nature, and inherent radioactivity.
Uranium as a natural element is found mostly in rock, soil, and water sources in small quantities. Uranium is classified as part of the actinide series and its specific isotope is 235U.
It is more abundant than antimony, beryllium, cadmium, gold, mercury, silver, or tungsten and has a similar level of abundance to arsenic. It is present in numerous minerals, including uraninite, which is the most prevalent uranium ore.
Join us in this article @Zik Natural Resources as we explore this unique element.
The Distinct Characteristics and Properties of Uranium
Uranium possesses distinctive qualities and captivating characteristics that are of great significance in several fields.
- Atomic structure: Uranium is an element represented by the chemical symbol U and has an atomic number of 92. It is a silvery-white heavy metal. Uranium atoms are composed of a compact nucleus around by circling electrons. Three isotopes of uranium occur naturally: uranium-238, uranium-235, and uranium-234. Out of these several isotopes, uranium-235 is especially noteworthy because, it can maintain nuclear fission processes (nuclear fission is a fundamental nuclear reaction in which the nucleus of an atom splits into two smaller, lighter nuclei. This process can occur spontaneously in some heavy elements or can be induced by bombarding the nucleus with neutrons or other particles), which makes it highly significant for generating energy and creating nuclear-powered weapons.
- Radioactivity: All the isotopes of uranium exhibit the property of being radioactive (the process by which an unstable atomic nucleus loses energy by emitting radiation), which indicates that they experience unprompted nuclear decay, releasing particles and energy as a result. The predominant decay process of Uranium-238, which is the most plentiful isotope, involves the emission of alpha particles, resulting in its conversion into thorium-234. Uranium-235 experiences alpha and beta decay, emitting alpha particles and beta particles, which leads to the formation of thorium-231. This sequence of radioactive decay is essential in the use of nuclear reactions and radiometric dating methods.
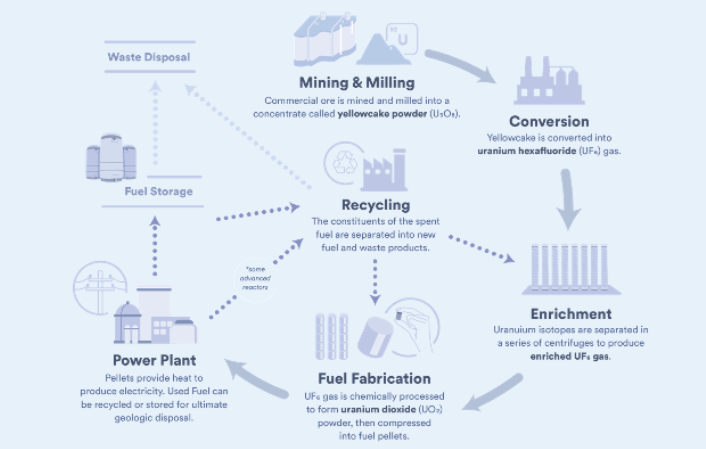
- Chemical Reactivity: Uranium demonstrates a moderate level of chemical reactivity since it undergoes slow reactions with oxygen, water, and acids in normal circumstances. It can create a range of chemical compounds, such as oxides, halides, and salts, depending on its level of oxidation. Uranium is typically found in the +4 and +6 oxidation states, with uranium dioxide (UO2) and uranium hexafluoride (UF6) being prominent examples. The chemical characteristics of uranium play a vital role in several activities such as uranium mining, processing, and nuclear fuel manufacturing, and involve the cleaning up of the environment to reduce uranium pollution.
Subscribe Now to www.zikresources.com for more educative and intriguing content.
The Role 0f Uranium as a Sustainable Energy Source
- Bountiful Resources: Uranium, an element that occurs naturally, is sufficient in the Earth’s crust, with substantial quantities found in different places around the world. The predicted uranium deposits are sufficient enough to last for generations, guaranteeing a dependable and durable energy source.
- Reduction of carbon dioxide emissions: Uranium as a source of energy has a remarkably low carbon footprint, making it highly appealing. Nuclear power generation emits negligible amounts of greenhouse gases while functioning, making it a crucial contributor to climate changes mitigation and overall adverse environmental effects reduction.
- The energy density and effectiveness: of nuclear-powered plant allows for the generation of massive amounts of electricity with just a little fuel. One kilogram of uranium-235, the primary isotope utilized in nuclear reactors, can generate millions of times more power, compared to the combustion of coal or natural gas. The increased energy density leads to improved energy production effectiveness, which in turn reduces resource utilization and waste formation.
Subscribe Now to www.zikresources.com for more valuable content.
The Essential Uses Of Uranium In The Society
Uranium possesses a wide range of potential uses that benefit scientific growth, industrial utilization, and societal advancement.
- Uranium-238 is utilized in radiometric dating methods to ascertain the chronology of geological structures, historic artefacts, and antique materials, offering vital knowledge about the past events of the Earth.
- Depleted Uranium is used in armour-piercing weapons and counterbalances because of its high density and ability to ignite spontaneously.
- Uranium compounds are used in glassware and ceramic production, which serves as catalysts in chemical reactions.
- Uranium-238, along with its decay products like radium-226 and radon-222, is used in brachytherapy and radiation treatment to specifically target and eliminate cancerous cells.
- Some militaries utilize 238U as a covering to safeguard tanks and incorporate it into some bullet components.
- It is utilized as a source of energy for industrial nuclear power reactors, where the fuel is generally enriched with 235U to a concentration of 2-3 per cent.
- Uranium is utilized in different industries such as lighting components, photographic chemicals, phosphate fertilizers, and X-ray targets for generating high-energy X-rays and shielding against radiation.
Subscribe Now to www.zikresources.com and share on your different social media platforms.
In conclusion, Uranium serves as a potential symbol of optimism in the shift towards a viable and lasting energy source. The wide range and relevance of uranium are seen in its various uses.
Although nuclear energy remains the main area of attention for the use of uranium, continual technological developments and innovation are continuously broadening its potential uses in several industries.
Adopting nuclear energy as a crucial element of the energy combination sets the stage for a more promising and environmentally friendly future.
Contact www.zikresources.com for more information